Unlock The Secrets Of Non-Programmed Decisions: Discoveries And Insights
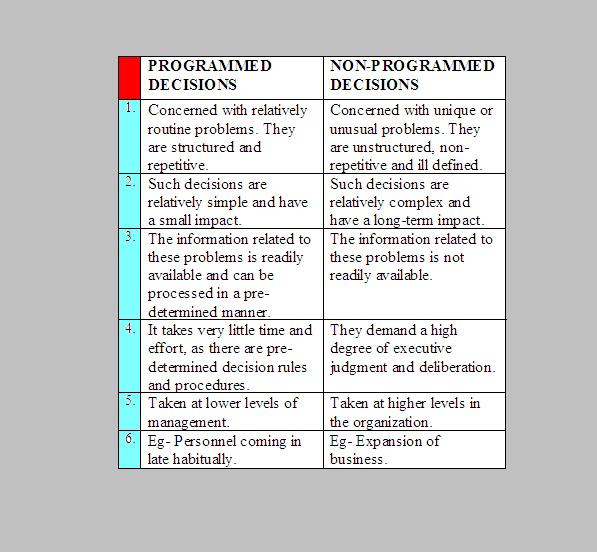
A non-programmed decision is a decision that is made without a predetermined plan or procedure. It is often made in response to an unexpected event or situation. Non-programmed decisions are often complex and require a great deal of creativity and judgment.
Non-programmed decisions are important because they allow us to respond to unexpected events and situations. They also allow us to be creative and innovative. Non-programmed decisions have been made throughout history, leading to some of the most significant advances in human civilization.
The main article topics will explore the different types of non-programmed decisions, the factors that influence them, and the process of making non-programmed decisions.
A Non-Programmed Decision
Non-programmed decisions are an important part of our lives. They allow us to respond to unexpected events, be creative, and innovate. Here are 10 key aspects of non-programmed decisions:
- Unstructured
- Novel
- Complex
- Ill-defined
- Discretionary
- Judgmental
- Intuitive
- Creative
- Innovative
- Strategic
Non-programmed decisions are often made in response to unexpected events or situations. For example, a manager may need to make a non-programmed decision about how to deal with a sudden increase in demand for a product. Non-programmed decisions can also be made in situations where there is no clear or easy solution. For example, a doctor may need to make a non-programmed decision about how to treat a patient with a rare disease.
Non-programmed decisions are important because they allow us to respond to unexpected events and situations. They also allow us to be creative and innovative. Non-programmed decisions have been made throughout history, leading to some of the most significant advances in human civilization.
Unstructured
Unstructured decisions are those that are made without a predetermined plan or procedure. They are often made in response to unexpected events or situations, and they require a great deal of creativity and judgment.
Non-programmed decisions are unstructured because they do not have a clear set of rules or guidelines to follow. This can make them difficult to make, but it also gives decision-makers the freedom to be creative and innovative.
For example, a manager may need to make an unstructured decision about how to deal with a sudden increase in demand for a product. There is no clear set of rules to follow in this situation, so the manager must use their judgment to make the best decision possible.
Unstructured decisions are an important part of our lives. They allow us to respond to unexpected events and situations, and they allow us to be creative and innovative. However, unstructured decisions can also be challenging, so it is important to have a good understanding of the factors that influence them.
Novel
Novel decisions are those that are new and have not been made before. They are often made in response to unique or unprecedented situations, and they require a great deal of creativity and innovation.
Novel decisions are an important part of non-programmed decisions. This is because non-programmed decisions are often made in situations where there is no clear or easy solution. In these situations, decision-makers must be able to think creatively and come up with new and innovative solutions.
For example, a company may need to make a novel decision about how to enter a new market. There is no clear set of rules to follow in this situation, so the company must be creative and innovative in order to develop a successful strategy.
Novel decisions can also be made in personal life. For example, a person may need to make a novel decision about how to deal with a difficult personal situation. There is no clear set of rules to follow in this situation, so the person must be creative and innovative in order to find a solution that works for them.
Making novel decisions can be challenging, but it is also an important part of life. Novel decisions allow us to respond to new and unique situations, and they allow us to be creative and innovative. However, novel decisions can also be risky, so it is important to weigh the risks and benefits before making a decision.
Complex
A non-programmed decision is a decision that is made without a predetermined plan or procedure. It is often made in response to an unexpected event or situation. Non-programmed decisions are often complex and require a great deal of creativity and judgment.
Complexity is closely associated with non-programmed decisions. This is due to the fact that when faced with a non-programmed decision, there is no clear or easy solution. As a result, decision-makers must take into account a wide range of factors and come up with a creative and innovative solution.
Example: A company may need to make a non-programmed decision about how to enter a new market. There is no clear set of rules to follow in this situation, so the company must be creative and innovative in order to develop a successful strategy.
Understanding the connection between complexity and non-programmed decisions is important because it allows us to better understand the decision-making process. It also allows us to develop better strategies for making complex decisions.
Ill-defined
A non-programmed decision is a decision that is made without a predetermined plan or procedure. It is often made in response to an unexpected event or situation. Non-programmed decisions are often complex and require a great deal of creativity and judgment. Ill-defined is closely associated with non-programmed decisions because when faced with a non-programmed decision, the problem or situation is often not clearly defined. This can make it difficult to identify the relevant factors and develop a solution.
For example, a company may need to make a non-programmed decision about how to enter a new market. The problem is ill-defined because there is no clear set of rules to follow. The company must be creative and innovative in order to develop a successful strategy.
Understanding the connection between ill-defined and non-programmed decisions is important because it allows us to better understand the decision-making process. It also allows us to develop better strategies for making complex decisions.
Discretionary
In the context of non-programmed decisions, discretion refers to the freedom and authority granted to decision-makers to exercise their judgment and make choices based on their own knowledge, experience, and understanding of the situation.
- Decision-Making Authority
Discretionary decisions are characterized by the decision-maker's autonomy to make choices without being bound by strict rules or procedures. This authority empowers them to consider various factors, evaluate alternatives, and ultimately select the course of action they deem most appropriate.
- Expertise and Experience
When making discretionary decisions, individuals often rely on their specialized knowledge and accumulated experience in the relevant field. Their expertise allows them to assess the situation, identify potential solutions, and make informed judgments.
- Accountability and Responsibility
While discretionary decisions grant decision-makers a degree of freedom, they also come with a sense of accountability and responsibility. Individuals making these decisions are expected to justify their choices, explain their rationale, and be answerable for the outcomes.
- Balancing Structure and Flexibility
Discretionary decision-making strikes a balance between structured processes and the need for flexibility. It allows for adaptability and responsiveness to unforeseen circumstances while ensuring that decisions are made within certain boundaries and with appropriate consideration.
In summary, the discretionary aspect of non-programmed decisions highlights the role of decision-makers' judgment, expertise, and accountability in navigating complex and novel situations. It empowers them to make choices that are tailored to the specific context while maintaining a sense of responsibility and adherence to broader organizational goals.
Judgmental
In the context of non-programmed decisions, judgment refers to the cognitive process of making choices based on subjective evaluations, personal experiences, and intuitive understanding of a situation.
- Subjective Evaluations
When making judgmental decisions, individuals rely on their own subjective interpretations and assessments of the situation. These evaluations are influenced by personal beliefs, values, and past experiences.
- Intuitive Understanding
Non-programmed decisions often require decision-makers to draw upon their intuitive understanding of the situation. This intuitive sense helps them grasp the underlying dynamics and make choices based on their "gut feeling" or subconscious insights.
- Balancing Objectivity and Subjectivity
While judgmental decisions involve subjective evaluations, it is important to strive for a balance between objectivity and subjectivity. Decision-makers should consider relevant data, consult with experts, and be open to different perspectives to minimize biases and enhance the quality of their judgments.
- Responsibility and Accountability
As with other aspects of non-programmed decisions, judgmental choices come with a sense of responsibility and accountability. Decision-makers must be able to justify their decisions, explain the rationale behind their choices, and take ownership of the outcomes.
Overall, the judgmental aspect of non-programmed decisions highlights the role of subjective evaluations, intuitive understanding, and the need to balance objectivity and subjectivity. It emphasizes the importance of decision-makers being accountable for their choices and being able to articulate the thought process behind their judgments.
Intuitive
Intuition plays a significant role in non-programmed decisions, which are characterized by their unstructured, novel, and complex nature. It refers to the ability to make choices based on subconscious insights, gut feelings, and past experiences, without relying solely on logical reasoning or structured analysis.
- Rapid Decision-Making
In situations where time is of the essence and there is limited information available, intuition can facilitate rapid decision-making. It allows individuals to make quick judgments and take immediate action, often based on their accumulated knowledge and experience in similar situations.
- Pattern Recognition
Our subconscious mind is adept at recognizing patterns and making connections that may not be immediately apparent through conscious analysis. Intuition can help decision-makers identify underlying patterns in complex situations and make informed choices based on those insights.
- Creative Solutions
Non-programmed decisions often require creative and innovative solutions. Intuition can help decision-makers break away from conventional thinking and explore new possibilities. By tapping into their subconscious, they may come up with novel ideas and solutions that might not be easily accessible through logical reasoning alone.
While intuition can be a valuable asset in non-programmed decision-making, it is important to note that it should be used in conjunction with other rational and analytical approaches. By combining intuition with logical analysis, decision-makers can make more informed and well-rounded choices.
Creative
In the context of non-programmed decisions, creativity plays a crucial role in finding innovative and effective solutions to complex and novel problems. Non-programmed decisions are those made without a predetermined plan or procedure, often in response to unexpected events or situations. Creativity, therefore, becomes essential in navigating these uncharted territories.
The connection between creativity and non-programmed decisions is evident in several ways. Firstly, creativity allows decision-makers to break away from conventional thinking and explore new possibilities. In situations where there are no clear guidelines or established solutions, creativity enables individuals to generate novel ideas and approaches.
Secondly, creativity fosters the ability to recognize patterns and make connections that may not be immediately apparent. By tapping into their creative thinking, decision-makers can identify underlying patterns in complex situations and develop innovative solutions that address the root causes of problems.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between creativity and non-programmed decisions lies in its application to real-world scenarios. In business, for instance, non-programmed decisions are often encountered in product development, marketing campaigns, and strategic planning. By embracing creativity, businesses can gain a competitive advantage by finding unique solutions to challenges and adapting to changing market dynamics.
In conclusion, creativity is an indispensable component of non-programmed decisions. It empowers individuals and organizations to navigate complex and uncertain situations by generating innovative solutions, recognizing patterns, and breaking away from conventional thinking. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective decision-making in a rapidly changing and increasingly complex world.
Innovative
Innovation stands as a cornerstone of non-programmed decisions, as it enables the creation of novel and groundbreaking solutions in the face of complex and uncertain situations. Non-programmed decisions, by their very nature, lack structured guidelines and clear paths, making innovation a critical tool for navigating these uncharted territories.
- Embracing Unconventional Approaches
Innovation often involves breaking away from conventional thinking and exploring uncharted territories. In non-programmed decision-making, this translates to the ability to challenge assumptions, question established norms, and seek inspiration from diverse sources to develop unique solutions.
- Harnessing Creativity and Imagination
Creativity and imagination serve as the fuel for innovation. Non-programmed decisions demand the ability to generate novel ideas, combine seemingly disparate concepts, and envision new possibilities. By embracing creativity, decision-makers can unlock a wider range of potential solutions and transformative outcomes.
- Adapting to Changing Circumstances
Non-programmed decisions often arise in dynamic and rapidly evolving environments. Innovation becomes essential for adapting to unforeseen changes, adjusting strategies, and finding solutions that remain effective amidst shifting circumstances. By fostering a culture of innovation, organizations and individuals can stay agile and responsive to the ever-changing landscape.
- Gaining Competitive Advantage
In today's competitive business environment, innovation can provide a significant edge. By leveraging innovative approaches to non-programmed decisions, organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, disrupt markets, and establish themselves as leaders in their respective industries.
In conclusion, innovation is inextricably linked to non-programmed decisions. By embracing unconventional approaches, harnessing creativity, adapting to changing circumstances, and seeking competitive advantage, decision-makers can navigate the challenges of non-programmed situations and drive transformative outcomes.
Strategic
In the context of non-programmed decisions, "strategic" refers to the long-term, high-level thinking and planning that goes into making complex and impactful choices. Non-programmed decisions, by their very nature, lack clear guidelines and structured approaches, making strategic thinking crucial for navigating these uncertain situations effectively.
The connection between "strategic" and "a non-programmed decision" is evident in several ways. Firstly, strategic thinking enables decision-makers to consider the broader context and long-term implications of their choices. In non-programmed situations, where the path forward is unclear, strategic thinking provides a framework for evaluating options, anticipating potential consequences, and aligning decisions with overall organizational goals.
For instance, a company facing a sudden shift in market dynamics may need to make a non-programmed decision about whether to enter a new market or invest in. Strategic thinking would involve analyzing the market landscape, assessing the company's strengths and weaknesses, and considering the potential risks and rewards of each option. By taking a strategic approach, the company can make an informed decision that aligns with its long-term vision and goals.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between "strategic" and "a non-programmed decision" lies in its application to real-world scenarios. In business, for example, non-programmed decisions are often encountered when companies face disruptions, changing customer preferences, or the need to innovate. By adopting a strategic approach, businesses can make well-informed decisions that not only address immediate challenges but also contribute to their long-term success and sustainability.
In conclusion, "strategic" is an essential component of "a non-programmed decision" as it provides a framework for thinking long-term, considering the broader context, and aligning decisions with overall organizational goals. By embracing strategic thinking, decision-makers can navigate the complexities of non-programmed situations and make choices that drive positive outcomes for their organizations.
FAQs on Non-Programmed Decisions
What is a Non-Programmed Decision?
A non-programmed decision is a decision made without a predetermined plan or procedure. It is typically made in response to an unexpected event or situation and requires a great deal of creativity and judgment.
When are Non-Programmed Decisions Made?
Non-programmed decisions are made when there is no clear or easy solution to a problem. They are often made in response to unexpected events or situations, such as a sudden change in market demand or a technological breakthrough.
Who Makes Non-Programmed Decisions?
Non-programmed decisions are typically made by managers and other decision-makers who have the authority to make decisions without consulting with others.
What are the Benefits of Non-Programmed Decisions?
Non-programmed decisions can lead to innovative and creative solutions to problems. They can also help organizations to adapt to changing circumstances.
What are the Challenges of Non-Programmed Decisions?
Non-programmed decisions can be difficult to make, as there is no clear or easy solution. They can also be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
How Can I Make Better Non-Programmed Decisions?
There are a number of things you can do to make better non-programmed decisions. These include:
- Gather all relevant information.
- Identify the key issues.
- Generate a list of possible solutions.
- Evaluate the pros and cons of each solution.
- Make a decision and implement it.
Conclusion
Non-programmed decisions are an important part of business. By understanding the benefits and challenges of non-programmed decisions, you can make better decisions that will lead to positive outcomes for your organization.
Next Article:The Non-Programmed Decision-Making Process
Tips on Non-Programmed Decision Making
Non-programmed decisions are complex and challenging, but they are also essential for businesses to adapt to changing circumstances and achieve success. By following these tips, you can make better non-programmed decisions that will lead to positive outcomes for your organization:
Tip 1: Gather all relevant information.
Before you can make a decision, you need to have all the relevant information. This includes understanding the problem, the available options, and the potential consequences of each option.
Tip 2: Identify the key issues.
Once you have all the information, you need to identify the key issues. These are the most important factors that you need to consider when making your decision.
Tip 3: Generate a list of possible solutions.
Once you have identified the key issues, you can start to generate a list of possible solutions. Be creative and open-minded, and don't be afraid to think outside the box.
Tip 4: Evaluate the pros and cons of each solution.
Once you have a list of possible solutions, you need to evaluate the pros and cons of each one. Consider the potential benefits and risks of each solution, as well as its feasibility and cost.
Tip 5: Make a decision and implement it.
Once you have evaluated the pros and cons of each solution, you can make a decision. Once you have made a decision, it is important to implement it quickly and effectively.
Conclusion
Non-programmed decisions are an important part of business. By following these tips, you can make better non-programmed decisions that will lead to positive outcomes for your organization.
Conclusion
A non-programmed decision is a decision made without a predetermined plan or procedure. It often requires creativity, judgment, and a deep understanding of the situation at hand. Non-programmed decisions are often made in response to unexpected events or situations, and they can have a significant impact on the success of an organization.
This article has explored the different aspects of non-programmed decisions, including their benefits, challenges, and how to make better non-programmed decisions. By understanding the importance of non-programmed decisions, organizations can make better decisions that will lead to positive outcomes.
Unraveling The Personal Life Of Josh Heupel: Unmasking His Beloved Wife
Unveiling The Bond: Brian Malarkey's Marital Journey Explored
Unveiling The Secrets: Exploring Somara Theodore's Salary Insights
ncG1vNJzZmiZl6TAqbXPZ5imq2NjsaqzyK2YpaeTmq6vv8%2Bamp6rXpi8rnvAZqWopl2lv7Cz0Zqkpp2UYrGmr8isoKimXp3Brrg%3D